5. The allocation of costs takes place in 2 stages:
a) Stage 1: Analysis and allocation of accounting expenditure related to processes/activities/regulation areas/entities outside ICP-ANACOM.
b) Stage 2: Allocation of expenditure to the different types of activity according to the acts underlying article 105 of Law No 5/2004, and related to sectors outside the scope of the Electronic Communications Law.
Figure 2: Stages of ICP-ANACOM’s cost allocation method
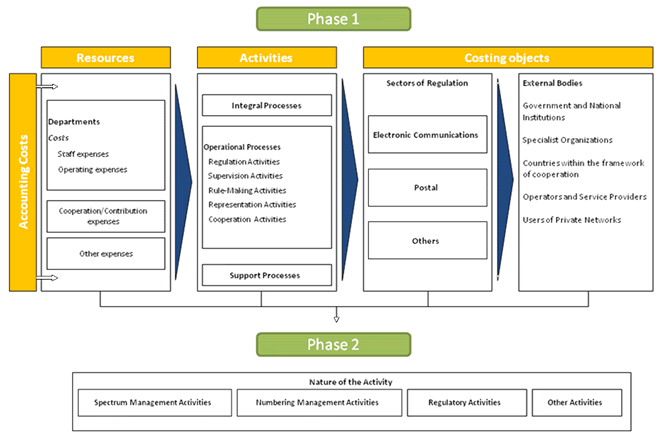
Phase 1: Analysis and allocation of accounting expenditure to ICP-ANACOM's processes/activities
6. First, expenditure is listed by groups and by department according to the following classification:
a) Direct resources - expenditure directly related to regulation services, through a cause- effect relation.
b) Indirect/common expenditure - expenditure not directly related to the regulation services.
c) Expenditure related to cooperation and levy - ICP-ANACOM's specific cooperation and representation expenditure.
7. Second, expenditure is allocated to processes/activities in a direct way or through criteria that represent a cause-effect relation between the nature of the expense and the process (processes) it supports.
8. By way of example, we briefly present the sequence of movements for expenditure classification:
a) Listing of total accounting expenditure by nature and by department.
b) Classification of expenditure according to the structure of the work processes in force, regulated and non-regulated areas (services), and external entities (clients). Analysis and allocation of expenditure to the processes1/ services and costing objects/clients of ICP-ANACOM2.
c) Staff costs3 are directly allocated to the processes /services and costing objects/clients of ICP-ANACOM, according to the report made by all employees on a computer application ''Reporte de Horas de Trabalho (RHT)'' - Working Hours Report.
d) Expenditure on travelling abroad, travelling within Portugal, advertising, specialized works, honoraria, training, documentation, meetings and sponsorships are directly related to the processes/services/clients, based on case-by-case relations, without prejudice to an irrelevant part being distributed according to the Man-Hours (MH) criterion.
e) Expenditure on electricity, water, air conditioning, rents of the head office facilities, installation insurance, elevators, cleaning, surveillance and security services costs are considered structure costs and are distributed according to the m2 used by each department. The remaining functioning expenditure, namely those related to economat, reprographics and communications, is distributed among all departments, according to their consumption4.
f) Expenditure on cooperation and contributions/levies5 are distributed according to the nature of the activity6.
g) Depreciation and amortisation expenditure of a relevant amount is associated with the work processes related to equipment, computer applications and hardware7, the remaining part being distributed by MH.
h) Provisions are treated similarly to common costs, being allocated to the several types of activity, according to the kind of provision8.
i) Other expenditure, for which a cause-effect relation may not be established, is distributed according to their relative cost or to MH.
9. It is important to stress that certain work processes, such as ''Planning and Control'', ''Financial System'', ''General Services'' and ''Human Resources'' do not have a direct relation to a specific regulation area, cutting across all areas9. For this reason, expenditure related to these work processes is redistributed to all operational processes, based on the criteria of relative costs or MH.
Phase 2 - Allocation of expenditure to the regulation sectors within the Electronic Communications Law
10. In order to ensure a correct allocation of accounting expenditure, by each regulation sector and within the scope of electronic communications, and by act broken down in paragraph 1 of article 105 of Law No 5/2004, a process was developed which enables this distribution, and which is identified as ''type of activity''.
11. The type of activity is identified according to a combination of work process/regulated area (service)/external entity (client)10. Each type of activity corresponds to a given set of combinations11.
12. The allocation of expenditure related to each type of activity follows the following process:
a) Identification of the amount of expenditure by item of type of activity (spectrum management activities, numbering management activities, regulation activities, and others).
b) Distribution of the amount of common costs (common accounting expenditure) and cooperation/levy costs by regulation item, considering one of the following options as a distribution criterion, bearing in mind the type of common/cooperation expenditure:
i ) Direct allocation to the corresponding item of type of activity through cause-effect relation.
ii ) Proportion of expenditure directly associated to each item of type of activity.
iii ) Proportion of MH allocated to each item of type of activity.
c) Afterwards, after determining the expenditure by each item of type of activity, the expenditure allocated to ''all activities'' of regulation is distributed among the following regulation sectors:
i ) Electronic Communications Sector;
ii ) Postal Sector;
iii ) Other sectors outside the scope of the Electronic Communications Law.
13. Subsequently, the costs determined at the level of the Electronic Communications Sector are distributed among acts defined in paragraphs a) to d) of article 105 of the Electronic Communications Law.
|
Types of Activity according to acts underlying article 105 of Law No 5/2004 |
||
|
Declarations supporting Rights |
Regulation |
|
|
Pursue of the activity - Regulation |
Regulation |
|
|
Allocation of Rights of Use for Frequencies |
Regulation |
|
|
Allocation of Rights of Use for Numbers and their Reservation |
Regulation - Numbering |
|
|
Spectrum Management Activities |
Spectrum Management |
|
|
Numbering Management Activities |
Numbering Management |
|
|
Costs allocated to sectors outside the scope of Law No 5/2004 |
||
|
Declarations supporting Rights12 |
Regulation |
|
|
Pursue of the activity - Regulation13 |
Regulation |
|
|
Amateur and CB records and certificates14 |
Spectrum Management |
|
|
Allocation of Rights of Use for Numbers and their Reservation15 |
Regulation - Numbering |
|
|
Spectrum Management Activities16 |
Spectrum Management |
|
|
Numbering Management Activities17 |
Numbering Management |
|
|
Costs not directly related to the regulation activity |
||
|
Common Costs |
||
|
Common Costs - Spectrum Management Activities |
Spectrum Management |
|
|
Common Costs - Spectrum Management Activities - Services Law No 5/2004 |
Spectrum Management |
|
|
Common Costs - Spectrum Management Activities - Services not covered by Law No 5/2004 |
Spectrum Management |
|
|
Common Costs - Regulation Activities |
Regulation |
|
|
Common Costs - Regulation Activities - Services Law No 5/2004 |
Regulation |
|
|
Common Costs - Regulation Activities - Services not covered by Law No 5/2004 |
Regulation |
|
|
Common Costs - Numbering Management Activities |
Numbering |
|
|
Common Costs - Allocation of Rights of Use for Frequencies |
Regulation |
|
|
Common Costs - Allocation of Rights of Use of Numbers and their Reservation |
Regulation - |
|
|
Common Costs - Declarations supporting Rights |
Regulation |
|
|
Common Costs - All activities - To distribute based on direct cost |
|
|
|
Common Costs - All activities - To distribute based on MH |
|
|
|
Common Costs - All activities - To distribute other costing objects |
|
|
1 According to the Processes/Activities Dictionary that supports the report of working hours of all ANACOM employees in the ''Reporte de Horas de Trabalho (RHT)'' - Working Hours Report, and the cost classification. The RHT application provides ANACOM's overall Man-Hours (MH).
2 Combination process and/or service or costing object and/or client.
3 Except for costs related to the Christmas Party, Anniversary and similar events concerning employees which are treated like common costs (Common Costs type - All activities - To distribute other costing objects).
4 Being distributed to processes/services/clients according to each department's hours report (MH - Man Hours for each department).
5 Always linked to the ''Cooperation'' process and to a specific external body.
6 Part of these costs is not related to the regulation activity. Vide also List of Types of Activity (Figure 3).
7 For instance: the amortisation of SINCRER equipment (Integrated Remote Control System for Radio Stations) is associated with the ''Spectrum monitoring'' sub-process and all radiocommunications services.
8 It may be broken down on the basis of direct costs or MH. Provisions for ongoing legal proceedings accounted for in recent years have been regarded as Common Costs - Regulation Activities - Services Law No 5/2004 and Common Costs - Spectrum Management Activities - Services Law No 5/2004.
9 They are regarded as common processes.
10 In some circumstances it is a function of the department that generated the cost.
11 According to the Processes/Activities Dictionary in use in ANACOM, that supports the costing system.
12 For the postal activity.
13 Postal Services and ITED.
14 Records and certificates related to CB (citizen band) and amateur service.
15 Audiotext and premium services.
16 CB and amateur service.
17 Audiotext services, added-value services and premium services.




