Portability
- Evolution in ported numbers
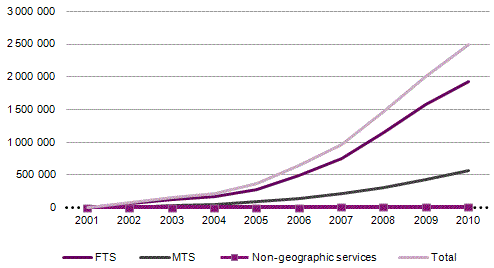
Since the introduction of portability (in 2001) and as on 31 December 2010, 2,494,859 numbers have been ported (1,928,892 geographic numbers, 564,126 mobile numbers and 1841 other non-geographic numbers, the latter including two numbers ported in the "30" numbering range associated with the nomadic VoIP service).
The graph below shows the growth rate of ported numbers for geographic numbers and mobile numbers; an uptick is seen in the rate growth since 2004, due to a higher level of FTS competition.
Graph 32 - Evolution in the number of ported numbers
Source: ICP ANACOM.
As in 2009, a low level of use of portability was reported in the mobile telephone service (MTS) during 2010. From 2009 to 2010, the rate of growth reported for mobile number portability (31.6 percent) exceeded the rate of growth reported for portability of geographic numbers (22.7 percent) but, in absolute terms, portability in the mobile service remains at a low level.
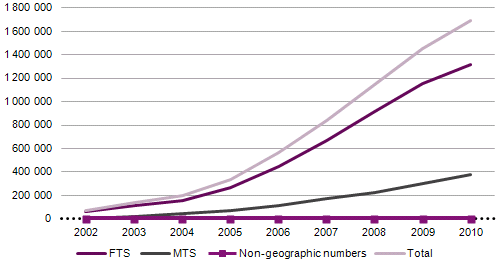
Evolution in terms of actual numbers ported (which reflects the quantity of numbers that are ported at any given time) is also shown, according to data recorded in the Reference Entity's database. Since portability can be used several times on the same number, where one client changes providers multiple times, including a return to their original provider, these values are lower than the values recorded in the previous graph.
As such, and as illustrated in the chart below, on 31 December 2010 there were 1,692,095 ported telephone numbers; this figure includes 1,314,178 geographic numbers (FTS), 376,445 mobile numbers (MTS) and 1,472 others non-geographic numbers (NGS) - this last category includes two ported numbers from the "30" numbering range.
Graph 33 - Evolution in the number of actual ported numbers in database
Source: ICP ANACOM.
The proportion of FTS and MTS assigned numbers that were ported and the proportion of FTS customers with ported numbers, as at the end of the second half of 2010, can be seen in the following tables, with information broken down according to segment (residential and non-residential):
|
|
End of 2nd half of 2010 |
|
I. Total |
17.5% |
|
II. Residential segment |
19.7% |
|
III. Non-residential segment |
14.9% |
Source: Responses from providers to the six-monthly portability questionnaire.
|
|
End of 2nd half of 2010 |
|
Proportion of direct access FTS customers with ported numbers |
15.5% |
Source: Responses from providers to the six-monthly portability questionnaire.
|
|
End of 2nd half of 2010 |
|
I. Total |
2.5% |
|
II. Residential segment |
1.3% |
|
III. Non-residential segment |
7.8% |
Source: Responses from providers to the six-monthly portability questionnaire.
- Evolution in portability deadlines between operators
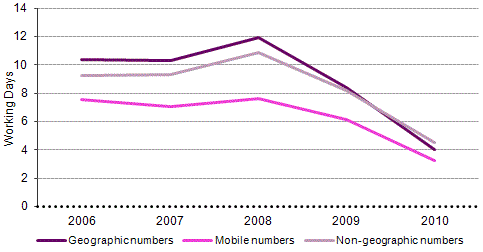
The entry into force of the new Regulamento da Portabilidade (Portability Regulation) had an immediate effect in making number portability quicker, as can be seen in the graphs below.
Although the established deadlines do not differ by type of number, there is a more significant reduction in the timings associated with mobile number portability, due in particular to the imposition of a limit of three days to fulfil the end-user's request, with compensation payable to the customer per day of delay. Meanwhile, geographic number portability has an inherent delay, which is frequently associated with loop unbundling or the deployment of the recipient operator's own infrastructure.
In the fourth quarter of 2010, portability timings in Portugal, for both FTS and MTS, were below the European average reported in 15th Implementation Report, which was given as 3.6 days and 3.2 days, respectively.
Graph 34 - Evolution of the deadlines for number portability
Source: ICP ANACOM.
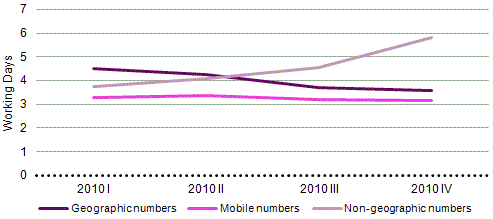
Graph 35 - Evolution reported in portability timings over 2010
Source: ICP ANACOM.
- Evolution in portability prices
ICP ANACOM compiled information from companies providing MTS (including mobile virtual network operators (MVNO)) and companies providing FTS on prices charged to subscribers for portability operations (retail prices) and on prices charged to recipient providers (wholesale prices).
According to the information collected and disclosed on ICP ANACOM's website, in the case of retail prices charged as at the end of 2010, it was found that, in general, MTS portability was provided free of charge (only one operator, in a business segment offer, reserves the right to charge a price of 30 euros per ported number). In the context of the FTS, it was found that nine out of fifteen providers of the service did not charge new customers who choose to keep their old number. The prices charged by FTS providers vary depending on the tariff plan or the market segment targeted, with a minimum value reported of 4.59 euros and a maximum value of 39.67 euros (excluding VAT). With respect to the nomadic VoIP service, it was found that portability is provided free of charge by six of the nine providers of this service, while the other three charge between 4.59 euros and 15 euros (excluding VAT).
In information compiled on wholesale prices, MTS and FTS providers, as well as providers of the nomadic VoIP service indicated that they charge the prices that are defined in the RIO, in accordance with the provisions of the Regulamento da Portabilidade (Portability Regulation).
Pre-selection
In line with the trend observed over recent years, the number of indirect access customers using pre-selection in 2010 continued to decline significantly, falling by about 20 percent since the end of 2009, as can be seen in the following graph.
Graph 36 - Evolution in the number of indirect access
customers using pre-selection
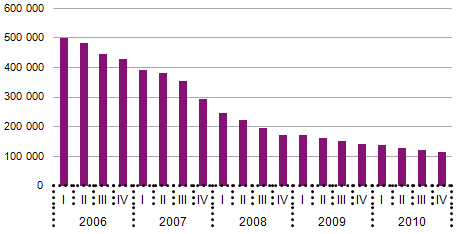
Source: ICP ANACOM.
This trend is due to the business plans of operators/service providers of electronic communications, which, in recent years, have focused on direct access (via their own network or via local loop unbundling) over indirect access.
1 Only numbers assigned to the end-customers of FTS providers themselves were considered. Numbers assigned to end-customers of other providers of electronic communications services using the numbering of the FTS providers were not considered.
2 Active mobile stations/user equipment is considered as mobile stations/user equipment which, at the end of the period under consideration is eligible to make use of one of the services available on mobile networks (i.e., it is eligible to make or receive voice calls or messages or to access a data transmission service), without necessarily being used. However, the numbers associated with the following categories were not considered: - mobile stations/user equipment associated with specific situations (operator tests, pre-active stations at agents/distributors, plans with minimum balance where no contractual relationship has been formalised, either by purchase of credits or by signing a contract); - user mobile stations/user equipment supporting, exclusively, the mobile broadband service.




